Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing the Condition
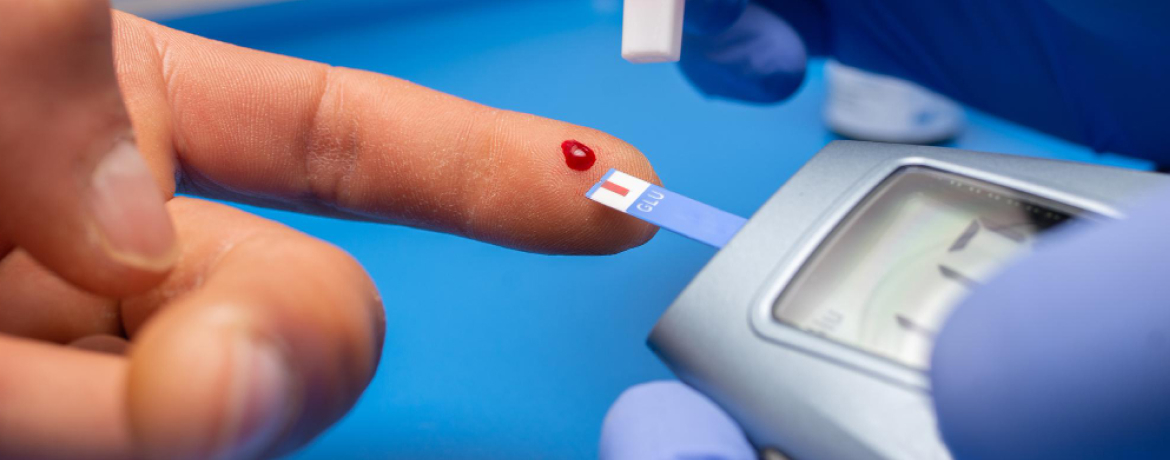
Diabetes is a prevalent and serious health condition affecting millions worldwide. According to a recent study, South Africa has experienced a significant increase in diabetes cases, with approximately 4.58 million adults living with the condition. This alarming statistic underscores the urgency of raising awareness about this chronic metabolic disorder and promoting effective management strategies. Managing diabetes is crucial for preventing complications and enhancing the quality of life for individuals living with the condition. Whether you or a loved one are among those diagnosed with diabetes, or you simply seek to learn more about this condition, here are a few practical tips to help you effectively navigate the challenges of diabetes and lead a fulfilling life with optimal health. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by elevated blood glucose levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. It facilitates the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used for energy production. In individuals with diabetes, this process is disrupted, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Diabetes is a complex and multifaceted condition, and there are different types of diabetes that individuals can experience. Each type has distinctive characteristics and requires specific management approaches. Here are the main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune condition. The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90-95% of all cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, and the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to compensate. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can still produce some insulin, but it is insufficient to control blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects some women who did not have diabetes before becoming pregnant. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance, and if the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand, gestational diabetes develops. Recognising the signs and symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early detection and prompt management. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. Various diagnostic tests, such as blood sugar level tests, A1C tests, and oral glucose tolerance tests, can help healthcare professionals determine the type and severity of diabetes. Living with Type 1 diabetes requires a proactive and diligent approach to ensure optimal health and well-being. Since the body cannot produce insulin, here are a few tips to regulate insulin levels and effectively manage the condition: Living with type 2 diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses lifestyle changes, medication management, and regular monitoring. Here are a few tips to help you manage the condition effectively: Gestational diabetes, a condition that develops during pregnancy, requires careful attention and proactive management to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby. While the diagnosis may initially bring concerns and uncertainties, rest assured that with the right strategies and support, you can effectively manage gestational diabetes and enjoy a healthy pregnancy. Don’t let distance or time constraints hold you back. Book an online consultation with our experienced diabetologists from anywhere, and receive personalised guidance to manage your condition effectively. Diabetes, if left unmanaged, can lead to various complications that impact overall health and quality of life. However, armed with knowledge and proactive measures, many of these complications can be prevented or minimised. Let’s delve into common diabetes-related complications and explore essential prevention strategies: Diabetes is a complex condition requiring lifelong management, but its impact can be minimised with a few lifestyle changes and proactive measures. By embracing a balanced diet, staying physically active, and closely collaborating with healthcare professionals, you can lead a fulfilling life while effectively managing diabetes. While this information does provide a general overview, please remember that individual needs and experiences can vary. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a care plan that suits your unique needs and lifestyle. Experience convenient and accessible online doctor consultations from the comfort of your home. Join now to connect with licensed healthcare professionals, receive personalised medical advice, and access top-notch care. Don’t wait – prioritise your well-being today! Sign up for Zarcare and embark on a journey to better health and wellness. Your well-being is just a click away! Experience convenient and accessible online doctor consultations from the comfort of your own home. Join now to connect with licenced healthcare professionals, receive personalised medical advice, and gain access to top-notch care. Don’t wait – prioritise your well-being today! Sign up for Zarcare and embark on a journey towards better health and wellness. Your well-being is just a click away! While no specific food can guarantee the prevention of type-2 diabetes, a balanced and nutritious diet can significantly reduce the risk. Here are five foods that you should include in your diet to reduce the risk of diabetes: Foods that are not good for diabetes and should be limited or avoided include: For most women, gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth. If it doesn’t go away after childbirth, the diabetes is referred to as type-2 diabetes. Moreover, gestational diabetes also increases the risk of developing type-2 diabetes in the later stages of life. Note: This article is not intended as a substitute for professional healthcare. If you suspect that you or someone you know is suffering from what is mentioned in this article, the Zarcare Team recommends contacting a qualified healthcare practitioner immediately to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/managing-diabetes/4-steps https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-management/art-20047963 https://www.careinsurance.com/blog/health-insurance-articles/diabetes-management-your-ultimate-guideUnderstanding Diabetes
Different Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes
Identifying Diabetes
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Gestational Diabetes
Diabetes Complications and Prevention
Take charge of your health with Zarcare!
Take charge of your health with Zarcare!
Frequently Asked Questions
References
